Every living creature is born, grows, and dies. Hair is no exception, but with a peculiarity: the hair growth cycle is a continuous alternation of death and rebirth. At least until the hair stops growing permanently.
Depending on the person, this cycle can be longer or shorter, and the “death” of the hair can occur sooner or later than expected.
The good news? There are ways to slow down this process.
Understanding the 4 phases of the hair cycle can help us unravel the mysteries of hair loss and promote hair growth.
What is the Hair Growth Cycle?
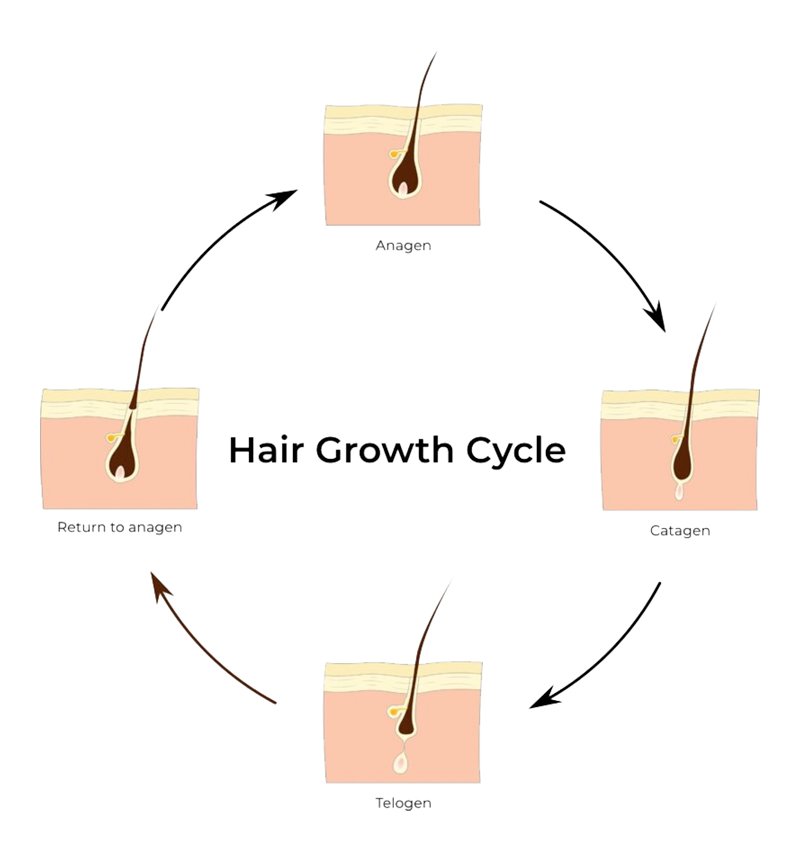
The hair growth cycle consists of four distinct phases: anagen, catagen, telogen, and exogen.
Each hair goes through this cycle independently, which means that while some are falling out, others are growing.
-
Anagen phase: the active growth period. Hair cells divide rapidly, and hair can grow for years.
-
Catagen phase: a brief transition in which growth stops and the follicle begins to shrink.
-
Telogen phase: the resting period. The hair remains in the follicle but does not grow.
-
Exogen phase: the shedding phase. The old hair is expelled to make way for a new one.
1. Anagen Phase of Hair Growth: The Active Period
The anagen phase is the crucial stage for hair growth, the longest and most important of the hair life cycle.
In this phase, the hair follicle is alive and active, producing new cells through rapid cell division.
How Long Does the Anagen Phase Last?
The anagen phase typically lasts from 2 to 6 years, but in some cases, it can extend up to 7 or even 10 years. The longer this phase lasts, the more the hair can grow.
Interestingly, body hair (such as eyebrows or arm hair) has a much shorter anagen phase - only 30-45 days - which is why it does not reach the length of scalp hair.
How to Extend the Anagen Phase of Growth?
To stimulate hair growth during the anagen phase, it is helpful to focus on the health of the scalp and follicles:
-
1. Scalp massages or microneedling to improve circulation.
-
2. Use of growth-promoting ingredients, such as Hair Rebirth strong products, minoxidil, caffeine, or peptides.
-
3. Low-level laser therapy (LLLT) can increase hair density.
-
4. A diet rich in protein, iron, biotin, and vitamin D.
- 5. Reduce stress, which can prematurely disrupt this phase.
Supporting scalp health is essential for keeping hair growing longer.
2. Catagen Phase of Hair Growth: The Transformation
The catagen phase is the shortest of the hair cycle and represents the transition between growth and rest. Only 1-3% of hair is in this phase at any given time.
During catagen, hair growth completely stops. The follicle shrinks and detaches from the blood supply, forming the so-called “club hair,” a fully formed hair that is no longer nourished, still anchored to the scalp.
How Long Does the Catagen Phase Last?
The catagen phase lasts about 2-3 weeks. It is a brief but crucial moment that marks the end of active growth and prepares the follicle for rest.
Being so quick, it often goes unnoticed. However, if many hairs enter catagen simultaneously (due to stress or illness), it could be a sign of telogen effluvium, a temporary form of hair loss.
3. Telogen Phase of Hair Growth: Everything Stops
The telogen phase is the resting period of the hair life cycle. The follicle becomes inactive, and the hair remains still without growing.
About 10-15% of your hair is in this phase at any time. Meanwhile, beneath the surface, new hairs begin to form, slowly pushing the old hair upward in preparation for shedding.
How Long Does the Telogen Phase Last?
The telogen phase generally lasts 3-4 months but can be prolonged due to stress, nutritional deficiencies, hormonal imbalances, or illnesses.
The duration depends on health and genetics; if too many hairs remain in telogen for too long, widespread thinning may be noticed.
4. Exogen Phase: Death of the Follicle and Shedding
The exogen phase is an extension of telogen: it is the moment when hairs actually fall out. The old club hairs are expelled while new hairs emerge from the follicle, initiating a new anagen cycle.
Losing 50-100 hairs a day in this phase is normal; a much higher number could indicate shedding issues.
How Long Does the Exogen Phase Last?
The exogen phase of hair growth lasts between 2 and 5 weeks, often overlapping with the end of telogen and the beginning of anagen.
During this period, more follicles may release hairs simultaneously.
How Long Does the Hair Growth Cycle Last
The duration of the hair growth cycle varies from person to person, but generally ranges from 2 to 7 years.
-
The anagen phase lasts from 2 to 6 years, depending on genetics and health.
- The catagen phase lasts about 2-3 weeks.
-
The telogen phase can last from 3 to 4 months.
-
The exogen phase overlaps with telogen and lasts a few weeks, during shedding.
A longer anagen phase means longer and thicker hair. The good news? There are ways to extend the anagen phase and delay the resting and shedding phases
- we will discuss this soon -.
Factors That Can Shorten the Anagen Phase
These factors can shorten the anagen phase, hasten the shedding in telogen, and weaken the follicle, leading to hair loss or thinning:
Physical Stress on the Scalp
-
Tight hairstyles (ponytails, braids, extensions) → traction alopecia
- Aggressive brushing or frequent heat styling
-
Excessive use of harsh chemical treatments (bleaching, perms)
Emotional and Psychological Stress
-
High cortisol levels from chronic stress push hair into telogen (telogen effluvium)
-
Anxiety and lack of sleep negatively affect the follicles
Poor Nutrition
-
Low protein intake → hair is made of keratin (a protein)
-
Deficiencies in iron, zinc, biotin, vitamin D, B12, omega-3
- Drastic diets or caloric restriction reduce energy to the follicles
Hormonal Imbalances
-
High levels of DHT (dihydrotestosterone) shrink the follicles → androgenetic alopecia
-
Thyroid disorders (hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism)
-
PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome) in women
-
Hormonal changes during menopause or postpartum
Medications that Affect Growth
-
Antidepressants (e.g., SSRIs)
-
Blood pressure medications (beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors)
-
Isotretinoin (for acne)
-
Chemotherapy
-
Birth control pill (start or stop)
Lifestyle and Environmental Factors
-
Smoking reduces blood flow to the follicles
-
Alcohol abuse interferes with nutrient absorption
-
UV rays from the sun damage the scalp
-
Pollution and toxins cause oxidative stress to the follicles
Genetic Conditions and Autoimmune Disorders
-
Alopecia areata: the immune system attacks the follicles
-
Androgenetic alopecia: baldness caused by family genetics
-
Lupus and other systemic inflammatory conditions
-
Trichotillomania: hair-pulling disorder

How Can I Stimulate Hair Growth?
When the hair cycle is disrupted - whether due to stress, hormones, or genetics - there are ways to stimulate hair growth, restore balance, and protect the follicles.
The best approach depends on the cause and severity of the problem.
1. Natural Solutions and Lifestyle
🔹 Nutritional Support Focus on proteins, iron, biotin, zinc, omega-3, and vitamin D. Supplements if blood tests show deficiencies.
🔹Stress Reduction Mindfulness, quality sleep, and less screen time reduce cortisol. Cortisol can push hair into telogen prematurely.
2. Medical Treatments
Ideal for those with progressive thinning or hair loss due to genetics, hormones, or chronic inflammation.
🔹Hair Rebirth: An innovative therapy and treatment resulting from years of study, research, and development.
Restores the hair life cycle in weakened follicles thanks to an advanced Trichological Formula that is the most complete in the world.
🔹 PRP Therapy (Platelet-Rich Plasma): uses the patient's blood to extract growth factors that are then injected into the scalp to awaken dormant follicles. Stimulates collagen and blood flow for the anagen phase.
🔹 Stem Cell Treatments: extracts stem cells (from adipose tissue or scalp biopsies) to regenerate the follicles. Available in advanced clinics.
🔹 Minoxidil and Finasteride: Minoxidil is a topical treatment to prolong the anagen phase. Finasteride is an oral medication that blocks DHT, used for male hair loss.
3. Hair Transplant Solutions
🔹 Stem Cell Transplant Combines traditional methods with stem cell therapy. Accelerates healing and stimulates hair growth in donor and recipient areas.
🔹 DHI (Direct Hair Implantation) Uses a Choi pen for precise graft placement. No channel openings; less trauma and quick recovery.
🔹 Sapphire FUE Technique Uses ultra-sharp sapphire blades for micro-channels. Minimally invasive, with natural results and high density.
🔹 Women's Transplant Customized for female hair loss patterns (often diffuse thinning). Focus on preserving the hairline and aesthetic harmony.
